Comprehensive Guide to Managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
This comprehensive overview explains irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), its causes, symptoms, and practical home remedies. It highlights common triggers like infections, diet, stress, and medications. The article offers effective strategies such as dietary adjustments, meal regulation, and cautious medication use to manage the condition. Remember to consult healthcare providers for personalized treatment. This guide aims to raise awareness and provide helpful tips for those affected by IBS, ensuring better understanding and management of symptoms.
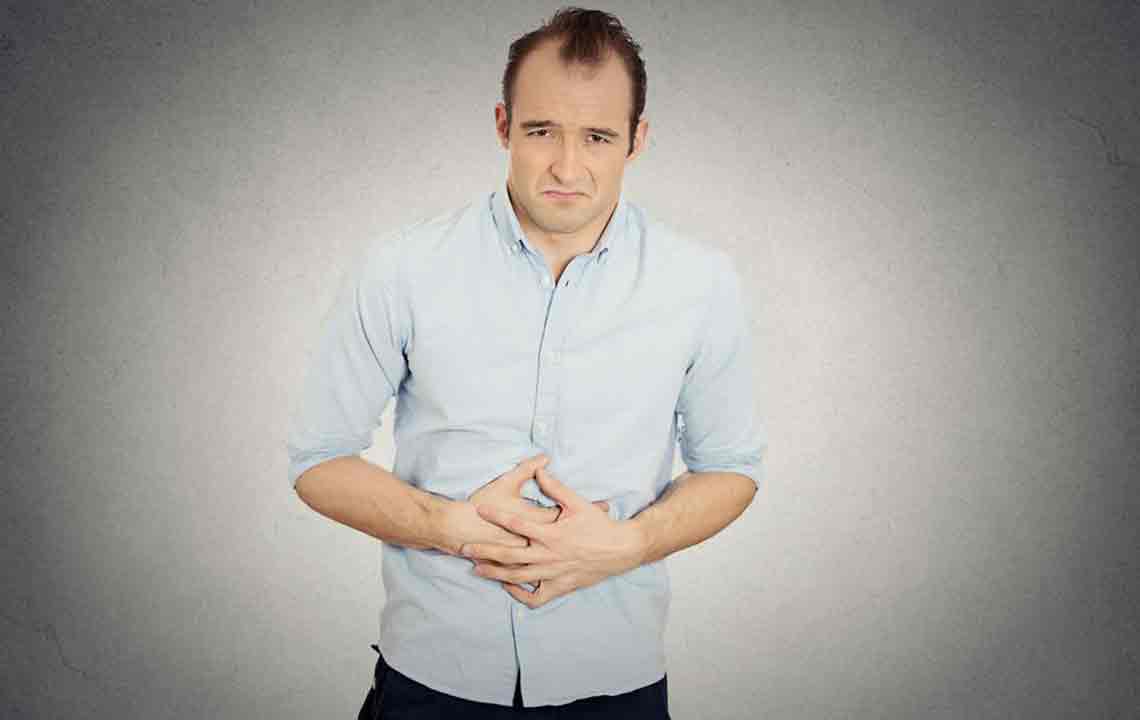

Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal discomfort, bloating, and irregular bowel movements ranging from diarrhea to constipation. Both children and adults can experience IBS. This guide summarizes vital information about the condition.
What is IBS?
Diarrhea-dominant IBS
Constipation-predominant IBS
Mixed IBS, with alternating diarrhea and constipation
Pain-centered IBS, marked by cramps and bloating
Common triggers of IBS
Viral infections such as Norwalk virus, hepatitis, or cytomegalovirus, particularly rotavirus in kids, can irritate the digestive tract.
Lactose intolerance leading to discomfort after dairy consumption due to enzyme deficiency.
Fruits and foods high in fructose, a natural sweetener, may cause issues for sensitive individuals.
Medications like antibiotics can disrupt gut bacteria balance, resulting in symptoms.
Contaminated food and water contaminated with bacteria like Salmonella or parasites such as Giardia may contribute to IBS.
Artificial sweeteners including sorbitol and mannitol found in sugar-free products can upset digestion.
Abdominal surgeries or gallbladder removal sometimes trigger IBS symptoms.
High stress levels are linked to increased susceptibility and severity of IBS.
Key symptoms of IBS
Symptoms include bloating, constipation with hard or lumpy stools, infrequent or painful bowel movements, diarrhea with frequent loose stools, and mucus in stool. Severe cases may involve blood in stool.
Home Strategies to Alleviate IBS
Increase dietary fiber: Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support digestion, but avoid excess if bloating persists.
Avoid trigger foods: Steer clear of greasy, spicy, processed, and fried foods to prevent flare-ups.
Regular meals: Keep consistent eating patterns; smaller, frequent meals help manage diarrhea, while larger meals assist with constipation.
Use medications cautiously: Opt for over-the-counter treatments wisely, and avoid unnecessary antibiotics that may harm gut bacteria.
Manage lactose intake: Reduce or eliminate dairy products if lactose intolerance is confirmed to ease symptoms.
Note: The information provided aims to offer practical advice on IBS management but is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Always seek advice from healthcare professionals for diagnosis and treatment plans. The website is not responsible for inaccuracies or third-party content.