Comprehensive Guide to Living with Lupus: Symptoms, Prevention, and Management
This comprehensive guide highlights lupus symptoms, preventive dietary choices, and lifestyle adjustments. It emphasizes early detection, immune-boosting nutrition, and regular activity to help manage this autoimmune condition effectively. Consulting healthcare professionals is recommended for personalized treatment plans.

Comprehensive Guide to Living with Lupus: Symptoms, Prevention, and Management
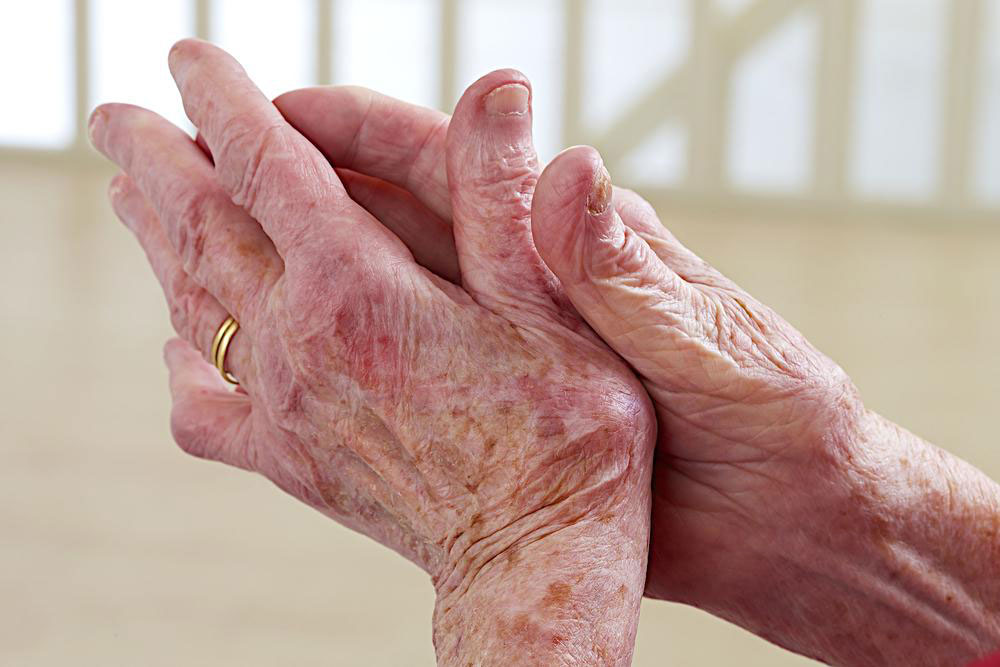
Lupus is a complicated autoimmune disease where the immune system erroneously attacks healthy tissues and organs, including the heart, joints, brain, lungs, kidneys, and hormonal glands such as the thyroid and adrenal glands. Approximately 90% of those affected are women. Common manifestations include skin rashes, persistent fatigue, headaches, mood disorders, joint pain, sleep disturbances, memory issues, and digestive problems. Adopting specific dietary and lifestyle habits can significantly aid in managing and mitigating lupus symptoms.
Identify Early Symptoms
Lupus can arise due to genetic predisposition or nutritional deficiencies. It typically affects individuals between 15 and 45 years old. Indicators include allergic reactions, hormonal imbalances, digestive issues, fatigue, joint stiffness, fever, mouth ulcers, vision problems, chest discomfort, skin rashes, elevated blood pressure, among others. Being aware of these early signs promotes prompt diagnosis and intervention.
Eat a Nourishing Diet
Prioritize organic, minimally processed foods, along with fresh vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins C and E. Include omega-3 sources like salmon and sardines, probiotic-rich foods, herbs, teas, coconut oil, and bone broth. Limit intake of refined oils, trans fats, gluten, processed meats, sugars, excessive salt, alcohol, caffeine, and certain legumes like peanuts and alfalfa. These can potentially aggravate symptoms.
Maintain Rest and Physical Activity
Aim for adequate sleep and incorporate regular exercise such as walking, aerobic routines, dancing, or Zumba for at least 15–30 minutes daily. Staying active and well-hydrated, combined with a balanced diet abundant in fruits and proteins, supports immune function and reduces flare-ups.
Avoid Certain Foods
Limit nightshade vegetables like eggplant, white potatoes, peppers, and tomatoes, as lupus patients often show sensitivity. Keeping a food diary can help track reactions. Reduce salt intake and steer clear of certain herbs and spices that may interfere with medication. A personalized diet emphasizing immune support can help lessen disease severity.
Understanding lupus and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential for effective management. Proper nutrition, rest, and physical activity bolster the body’s defenses against autoimmune responses.
Note:
This article provides evidence-based health advice but should not replace professional medical consultation. Always seek guidance from your healthcare provider before making lifestyle modifications.