A Guide to Normal Blood Cell Counts and Their Significance
This article explains normal blood cell levels, their functions, and importance for health. It covers white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets, highlighting their roles and typical ranges. Regular blood tests like CBC help detect abnormalities early, supporting overall health management. Medical consultation is advised if irregularities are identified, ensuring proper diagnosis and treatment. Maintain balanced blood cell levels for immune defense, oxygen transport, and clotting. A vital resource for understanding your blood health and its impact on wellbeing.

Understanding Normal Blood Cell Counts and Their Role in Health
Keeping blood cell levels within healthy ranges is essential for overall well-being. Healthcare providers often order a complete blood count (CBC) to assess white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets, which can reveal conditions like anemia, infections, or blood disorders, and help track treatments such as chemotherapy. The main blood cell types and their roles include:
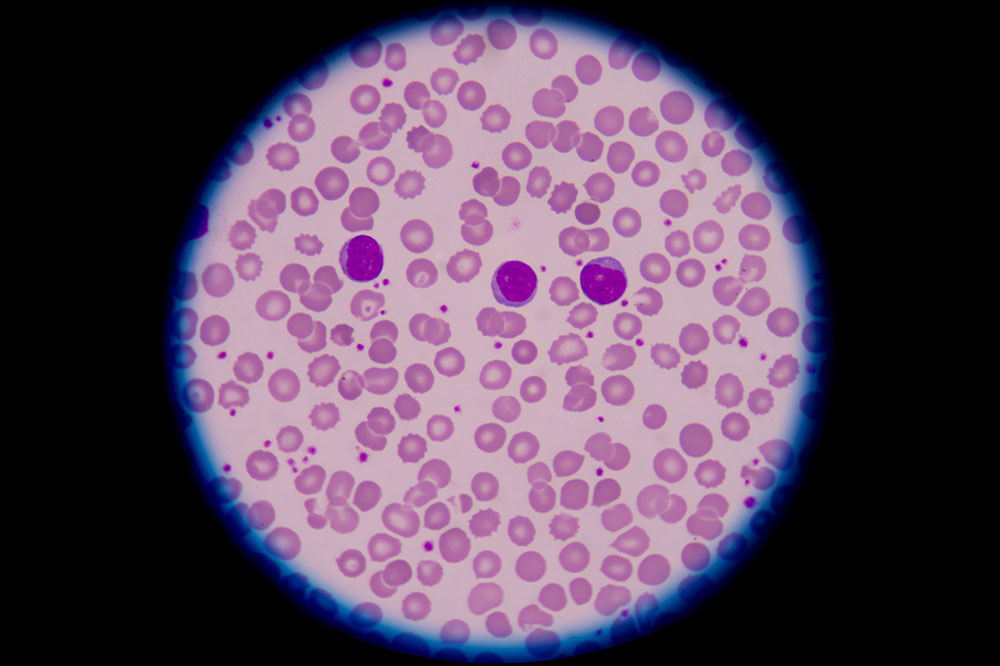
White Blood Cells (WBCs) – Essential for immune defense; high levels may indicate infection or inflammation, while low levels suggest vulnerability to infections. Normal WBC count ranges from 4,500 to 10,000 cells per microliter. Sudden or unexplained inflammation should prompt medical evaluation.
Red Blood Cells (RBCs) – Responsible for transporting oxygen and removing waste; low RBC levels can point to anemia. Normal counts are approximately 5 to 6 million per microliter in men and 4 to 5 million in women.
Platelets – Crucial for blood clotting; typical ranges are 140,000 to 450,000 cells per microliter. Monitoring platelet levels helps prevent bleeding or clotting complications.
Routine blood testing plays a key role in detecting any irregularities in these cell counts, which can significantly affect health. Annual CBC exams are recommended to ensure immune function, oxygen delivery, and coagulation are well-maintained. Contact your healthcare provider if abnormalities are found.
Note: This article offers general health insights based on reputable sources. It is not intended as medical advice. Always seek personalized guidance from your healthcare professional. We do not accept responsibility for discrepancies or updates in medical guidelines or sources.