Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Diabetes
This detailed guide explores diabetes, its causes, symptoms, potential complications, and preventive strategies. Emphasizing lifestyle modifications, it provides essential insights into managing this widespread metabolic disorder effectively. Understanding these aspects can help individuals take proactive steps to prevent and control diabetes, promoting better health outcomes worldwide.
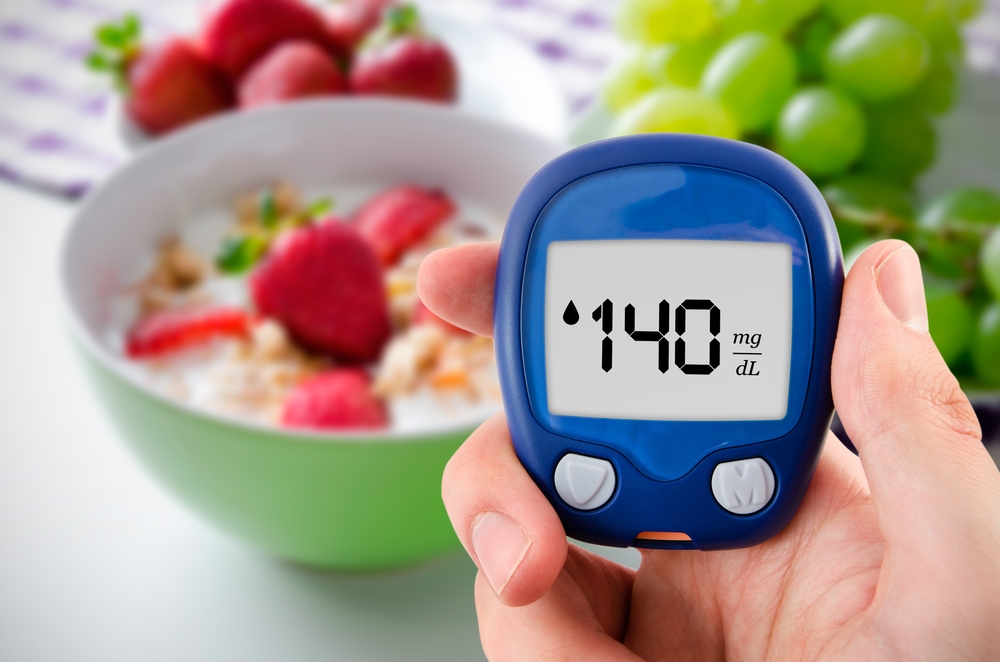

Key Knowledge for Effective Diabetes Care
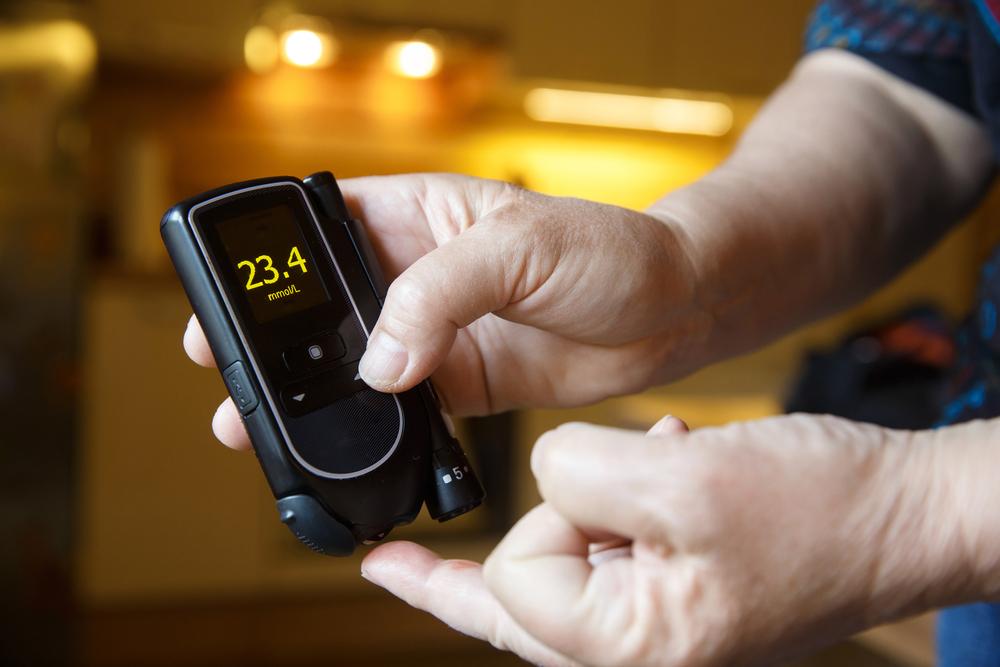
Diabetes is a widespread metabolic disorder impacting millions around the globe. It results from irregular blood glucose levels due to impaired insulin production or function. Insulin, a hormone from the pancreas, facilitates glucose conversion into energy. When insulin issues arise, excess sugar remains in the bloodstream, risking severe health complications. Genetics also play a significant role, affecting even newborns. Recognizing the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures is essential for controlling this chronic illness.
Factors like heredity, lifestyle choices, and environmental exposures influence diabetes development. While excess sugar intake isn't the sole factor, genetic predisposition significantly impacts risk. Other contributors include infections, obesity, physical inactivity, poor nutrition, autoimmune responses, toxins, pregnancy complications, and certain syndromes. Awareness of these causes aids in early detection and prevention.
Primary Causes of Diabetes
Individual risk factors, diet, and genetics shape the causes of diabetes. Common triggers include:
Viral or bacterial infections
Overweight and obesity
Sedentary lifestyles
Unhealthy eating habits
Autoimmune disorders
Food-related toxins
Pregnancy issues
Cushing's syndrome
Possible Diabetes-Related Complications
If left uncontrolled, diabetes can cause serious health conditions such as:
Eye problems like cataracts and retinopathy
Increased risk of skin infections and conditions
Mental health challenges including stress and depression
Hearing impairment
Gum disease
Delayed wound healing
Recognizing Diabetes Symptoms
Early signs can be subtle or sudden, especially in type 1 diabetes. Typical symptoms include blurry vision, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, increased hunger, slow-healing wounds, and frequent urination.
Preventive Approaches
Leading a healthy lifestyle significantly lowers the risk of developing diabetes. Important steps involve:
Regular physical activity, combining strength and cardiovascular training
Achieving and maintaining a balanced weight through nutritious diet
Routine medical checkups for early detection
Since there is no cure currently, lifestyle changes are crucial for prevention and effective management.tags – diabetes, prevention, health, blood sugar control
Disclaimer:
Our blog offers comprehensive health information for educational purposes. While based on research, it does not replace professional medical advice. For personalized guidance, consult healthcare providers. The content may not cover all available therapies or offers beyond our scope.