Top 5 Factors Influencing Mesothelioma Risk and Prevention
This article discusses the top five risk factors for mesothelioma, including asbestos exposure, zeolite dust, radiation therapy, SV40 virus, and genetic mutations. Early awareness and prevention strategies are essential for reducing risk and improving patient outcomes.
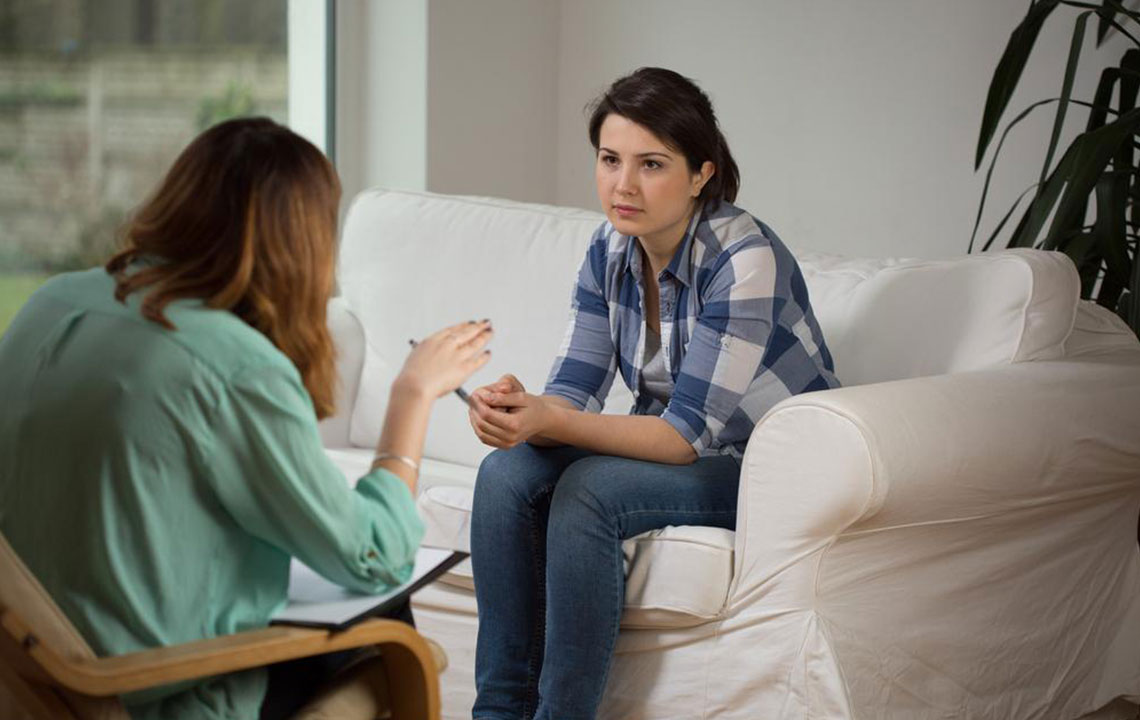

Mesothelioma is an aggressive cancer with limited survival chances, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis. Understanding the primary risk factors can help in timely intervention, improving patient outcomes.
Here are the main elements contributing to mesothelioma development:
Asbestos Contact: A leading cause, asbestos exposure accounts for over 80% of cases. Its resilient fibers, used in insulation and industrial products, pose inhalation or ingestion risks for workers involved in manufacturing or maintenance.
Zeolite Dust Exposure: Similar to asbestos, inhaling zeolite dust may increase mesothelioma risk. Proper protective gear and safety protocols are essential in environments with such mineral dust.
Radiation Exposure: Intense radiation therapy directed at the chest or abdomen has been linked to higher likelihood of developing mesothelioma later on.
SV40 Virus: Past contamination of some polio vaccines with the SV40 virus has been associated with increased disease risk.
Hereditary Factors: Genetic mutations, especially in the BAP1 gene, contribute to about 1% of cases and can be inherited.
Awareness of these risk factors aids in prevention and early detection. Always seek medical advice for screening and further guidance.