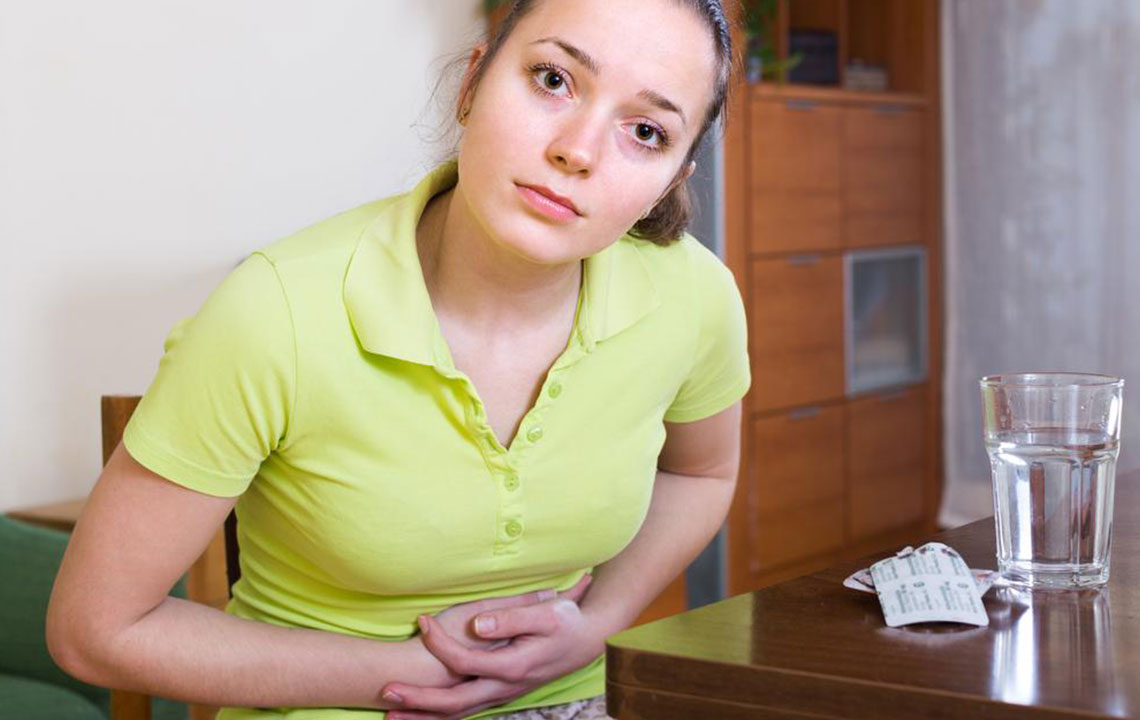
Understanding the Top 11 Causes of Constipation and How to Prevent It
Discover the top 11 causes of constipation, including diet, lifestyle, medications, and health issues. Learn preventive tips to maintain healthy bowel movements. Consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for personalized diagnosis and treatment strategies.

Understanding the Top 11 Causes of Constipation and How to Prevent It
Constipation can result from various health issues and lifestyle habits. Recognizing these factors is essential for effective management. Consulting a healthcare provider helps determine the underlying cause for targeted treatment.
Primary Causes of Constipation
A major contributor is the colon's tendency to absorb too much water, slowing stool movement. Weak or uncoordinated intestinal muscles can also delay bowel emptying and retain water. Consider these additional factors:
A diet low in fiber-rich foods like fruits, whole grains, and vegetables increases constipation risk. Adequate fiber intake supports regular bowel movements and alleviates discomfort.
Eating sufficient fiber helps maintain smooth bowel functions, reducing constipation chances. Foods low in fiber, such as processed meats, eggs, and dairy, may contribute to irregularities.
A sedentary lifestyle, common among older adults or hospitalized patients, can slow digestion. Regular movement activates bowel movements and prevents stagnation.
Certain medications, including opioids (like codeine and oxycodone), antidepressants (such as amitriptyline), anticonvulsants (e.g., phenytoin), and blood pressure drugs (like nifedipine), may cause constipation side effects. Some antacids with aluminum and diuretics are also culprits.
Excessive intake of dairy products, especially milk, can cause bowel irregularities and constipation in some individuals.
As people grow older, digestion slows, and muscle strength declines, making constipation more prevalent among seniors.
Changes in daily schedules, irregular eating habits, and sleep disturbances during travel can disturb bowel regularity, leading to constipation.
Overreliance on laxatives may weaken natural bowel function, causing dependency and infrequent, difficult evacuations when not used.
Suppressing the urge to defecate can lead to dry stool, making passage difficult and increasing constipation risk.
Proper water intake is vital; dehydration from caffeine, alcohol, or sugary drinks can harden stool and worsen constipation.
Conditions like tumors, diverticulosis, strictures, or congenital disorders (e.g., Hirschsprung disease) may cause physical obstructions leading to constipation.
Disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, diabetes, hypothyroidism, or autoimmune diseases can impair intestinal health. Cancer treatments may also contribute.