Essential Nutritional Approaches for Controlling Lupus Symptoms
This article offers practical nutritional tips for managing lupus symptoms effectively. Emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, fatty fish, and nuts, it guides patients on foods to include or avoid. Proper diet can reduce flare-ups, support immune health, and protect vital organs. Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized plans is advised for optimal management of this autoimmune condition.

Lupus is a persistent autoimmune disorder where the immune system erroneously targets healthy tissues, causing widespread inflammation and organ damage. Symptoms often include joint discomfort, skin rashes, fatigue, and kidney issues. While no cure exists, adopting specific dietary and lifestyle modifications can assist in managing symptoms and enhancing quality of life. Certain foods may either aggravate or relieve lupus symptoms, making mindful nutritional choices vital for effective disease control.
Comprehending Lupus
Lupus results from an exaggerated immune response that attacks the body's own tissues, leading to systemic inflammation. Proper nutritional management can help reduce flare-ups and promote overall well-being.
Maintaining a balanced, nutrient-rich diet with anti-inflammatory foods can help mitigate lupus symptoms and protect vital organs. Emphasizing antioxidant-rich foods, vitamins, and healthy fats is particularly advantageous. Simultaneously, avoiding foods that trigger inflammation is crucial for symptom control.
Foods Recommended for Lupus Management
To support health and decrease inflammation, consider including these in your diet:
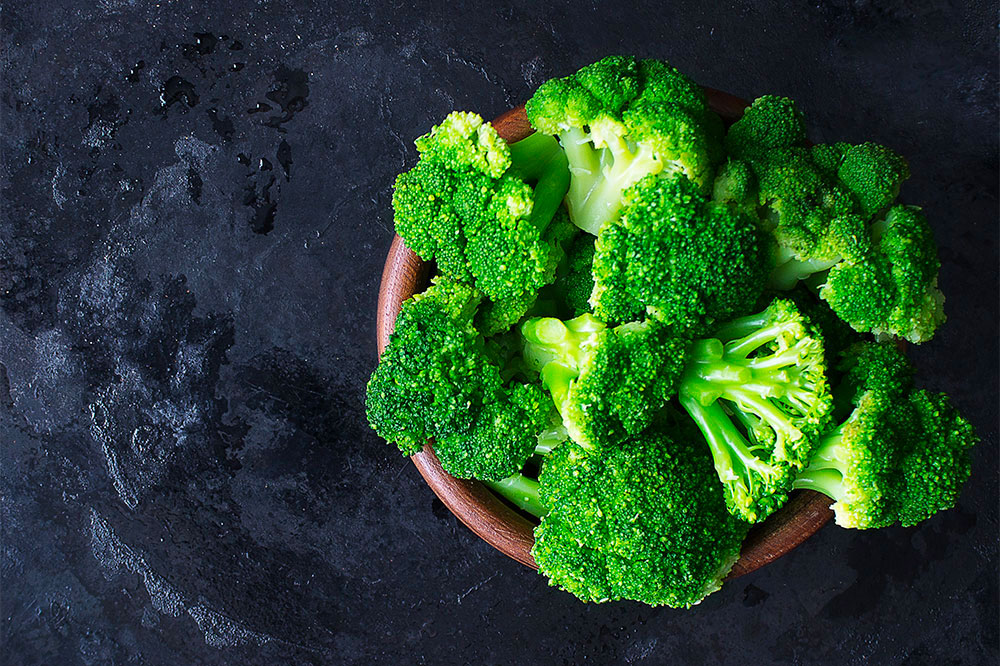
Green Leafy Vegetables
Spinach, kale, collard greens, broccoli, cabbage, and arugula offer antioxidants and vital nutrients like vitamins A, C, K, calcium, and iron, which can reduce inflammation and strengthen bones.
Whole Grains
Incorporate quinoa, brown rice, oats, and whole wheat products to provide fiber, complex carbohydrates, and nutrients that boost energy, digestion, and cardiovascular health—beneficial in lupus management.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Use for cooking or dressings. Rich in monounsaturated fats and polyphenols, it possesses anti-inflammatory properties and helps reduce oxidative stress.
Healthy Lipids: Avocados and Olives
These contain monounsaturated fats and omega-3s, known for anti-inflammatory effects and heart health. Avocados are also rich in potassium and vitamins to support immunity.
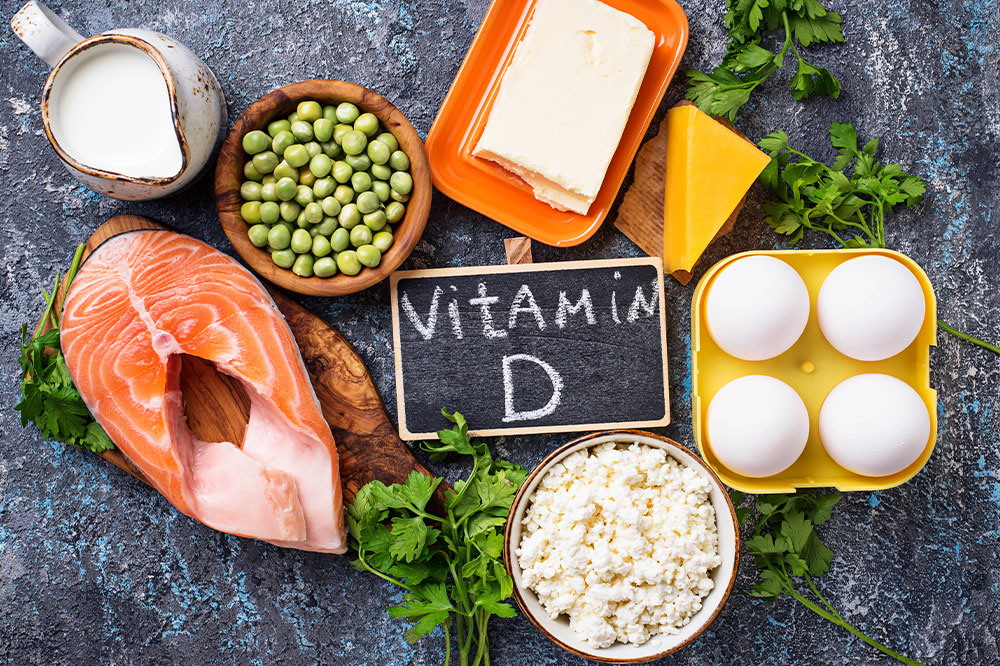
Fatty Fish
Include salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout into your meals. These are abundant in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D, which combat inflammation and support bone health.
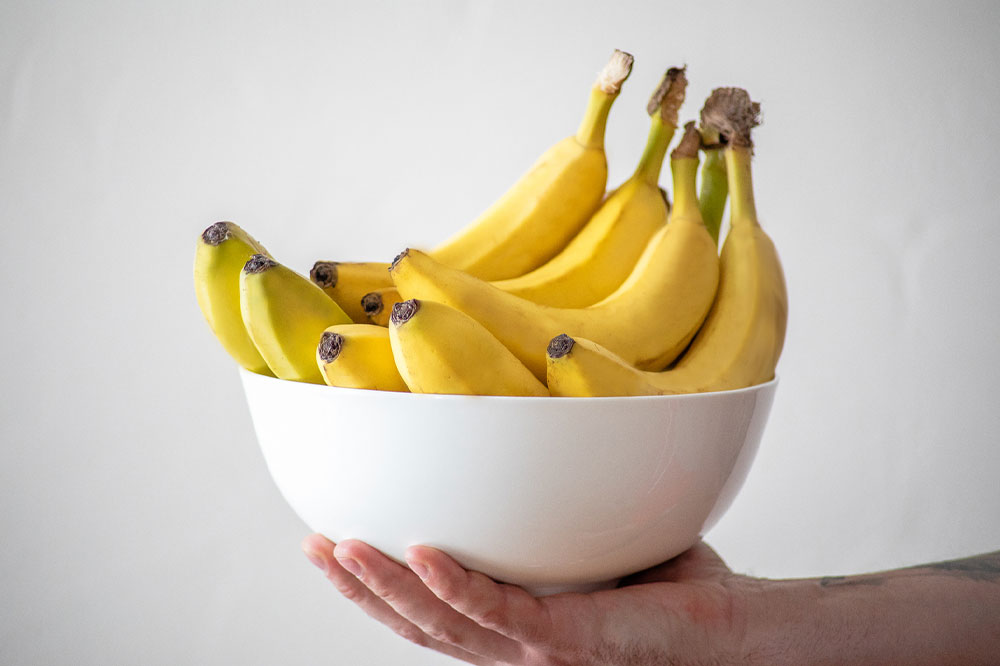
Fruits
Berries, citrus fruits, apples, and bananas provide antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber to boost immunity, improve skin, and reduce inflammation.
Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and pistachios supply essential fats, omega-3s, protein, and vitamins, offering lasting energy and cardiovascular benefits.
Legumes and Pulses
Black beans, lentils, and kidney beans deliver plant-based protein, fiber, and antioxidants to help stabilize blood sugar and diminish inflammation.
Calcium-Packed Foods
To maintain bone strength, include fortified plant-based milks, mushrooms, tofu, beans, yogurt, and leafy greens. Lactose-intolerant individuals should opt for plant options.
Foods to Limit or Exclude
Certain items may aggravate lupus symptoms or increase inflammation. These should be minimized or avoided:
Alfalfa Sprouts
Contain L-canavanine, which can activate immune responses and worsen inflammation.
Garlic
While immune-boosting, garlic can stimulate white blood cells and potentially flare autoimmune activity in lupus.
Red Meat
Rich in saturated fats, red meat may promote inflammation and elevate cardiovascular risks.
High-Sodium Foods
Processed meats, canned soups, soy sauce, and condiments can lead to fluid retention and increased blood pressure, worsening symptoms.
Fast and Processed Foods
Contain trans fats and additives that can trigger inflammation and flare-ups.
Sugar-Sweetened Drinks
Sodas and energy drinks spike blood sugar levels and promote inflammation; water or herbal teas are better alternatives.
Refined Carbohydrates
White bread and rice have high glycemic indexes, leading to blood sugar spikes and increased inflammation.
Customized dietary strategies and consultation with healthcare providers are essential. Making informed dietary choices can significantly aid in managing lupus symptoms and enhancing overall health.
Disclaimer:
The content provided here is for informational purposes only and should not substitute professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from healthcare professionals for personalized treatment and nutrition plans.