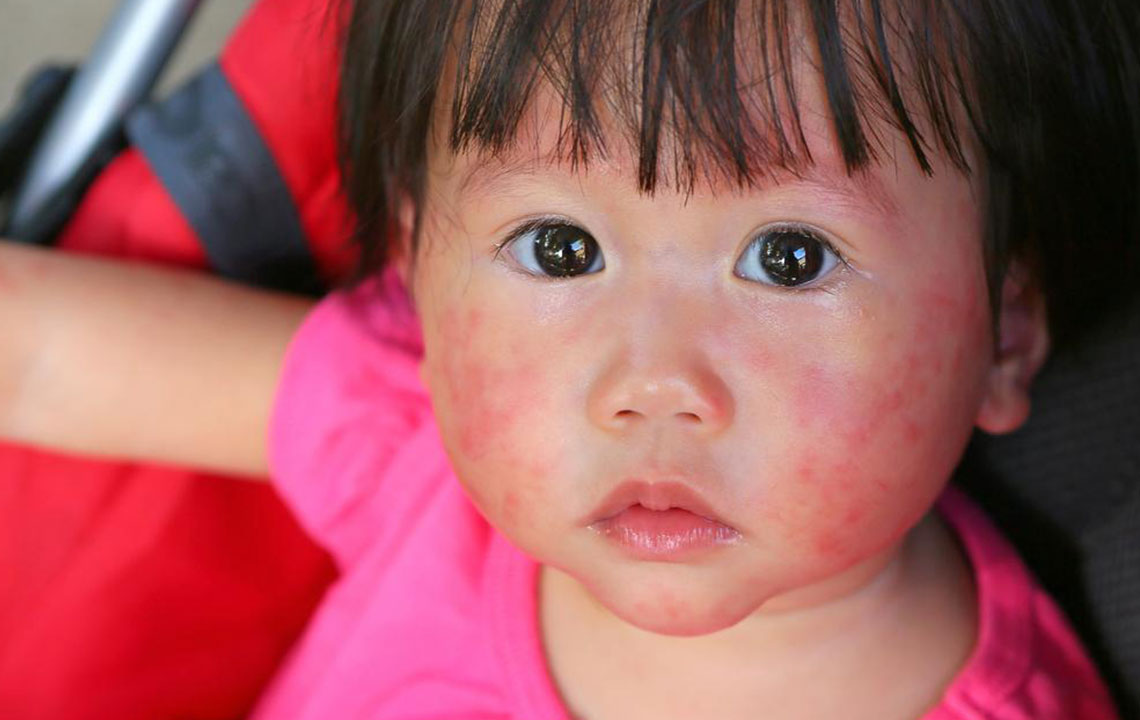
Top Strategies for Effectively Managing Childhood Eczema
Effective management of childhood eczema involves consistent skincare routines, hydration, gentle cleaning, and environmental controls. Regular doctor visits help tailor treatments, with options like moisturizers, medications, and light therapies for severe cases. Preventing flare-ups and secondary infections is crucial for maintaining skin health and comfort during childhood.
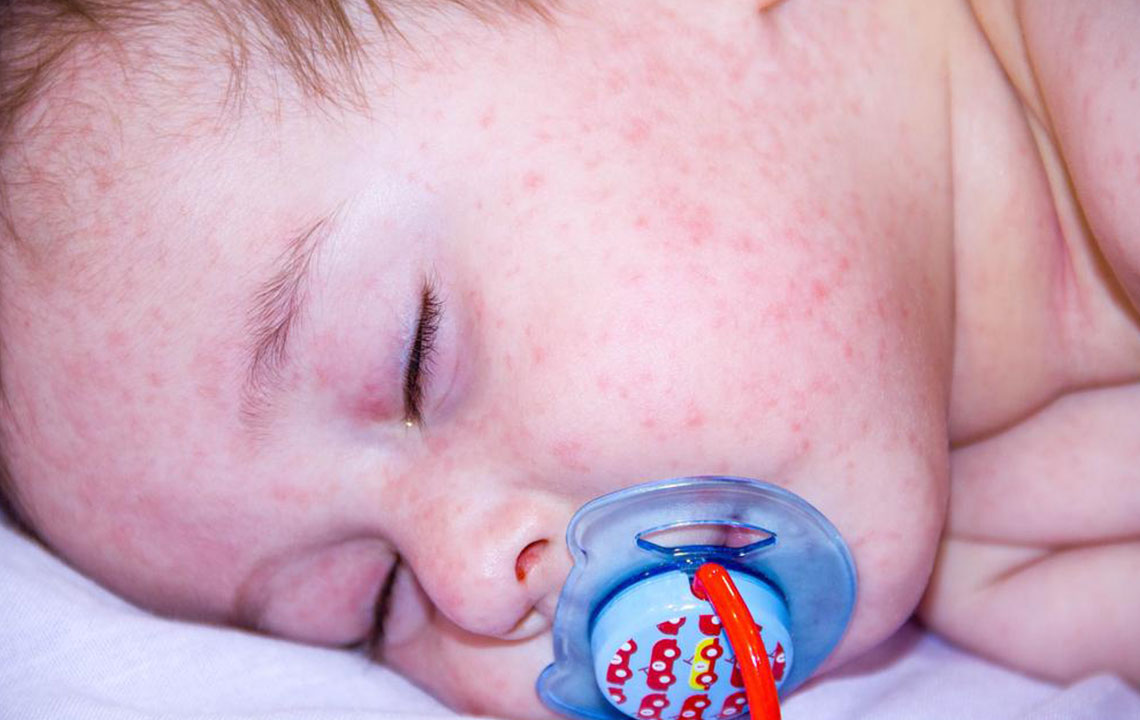
Top Strategies for Effectively Managing Childhood Eczema
Childhood eczema, primarily atopic dermatitis, is a common condition affecting those under two years old. This long-term skin disorder stems from genetic or immune factors, leading to itchy, red patches or small blisters. Symptoms can flare periodically and often improve over time, sometimes resolving by puberty. Effective management focuses on maintaining skin hydration, reducing inflammation, and ensuring comfort. Adopting a consistent skincare routine with moisturizers, gentle cleansing, and targeted medication when necessary can help control symptoms effectively.
The main objective is to keep the skin moist, avoid irritants, and prevent flare-ups. Proper skin care practices and environmental adjustments play vital roles in treatment.
Maintaining skin hydration is essential. Applying emollients forms a barrier against irritants and keeps skin moisturized. Using these lotions after baths helps prevent dryness and flare-ups. Regular moisturizer application significantly improves skin condition.
Bathing should be with lukewarm water, avoiding hot water that can dry out the skin. Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers with neutral pH. After bathing, gently pat dry and immediately apply moisturizer.
Antihistamines prescribed at night can help reduce itching and redness.
Minimize exposure to dust mites and irritants by keeping the environment clean. Dress children in soft cotton clothes and steer clear of synthetic fabrics that may worsen symptoms.
During flare-ups, topical corticosteroids can be applied carefully to inflamed areas to relieve symptoms.
If infections develop, doctors might recommend short courses of topical or oral antibiotics.
Periodic bleach baths (5-10 minutes) can prevent skin thickening and pigmentation issues.
Severe cases may require light therapy, such as psoralen combined with UV light, under medical supervision.
Routine check-ups are vital in assessing treatment progress. Seek medical advice if symptoms intensify or frequently recur to adjust care strategies.