Essential Guide to the Top 5 Fungal Skin Conditions
Learn about the top five common fungal skin infections, including their symptoms and prevention tips. This guide covers athlete’s foot, jock itch, candidiasis, pityriasis versicolor, and ringworm, emphasizing hygiene and moisture control for skin health.
Essential Guide to the Top 5 Fungal Skin Conditions
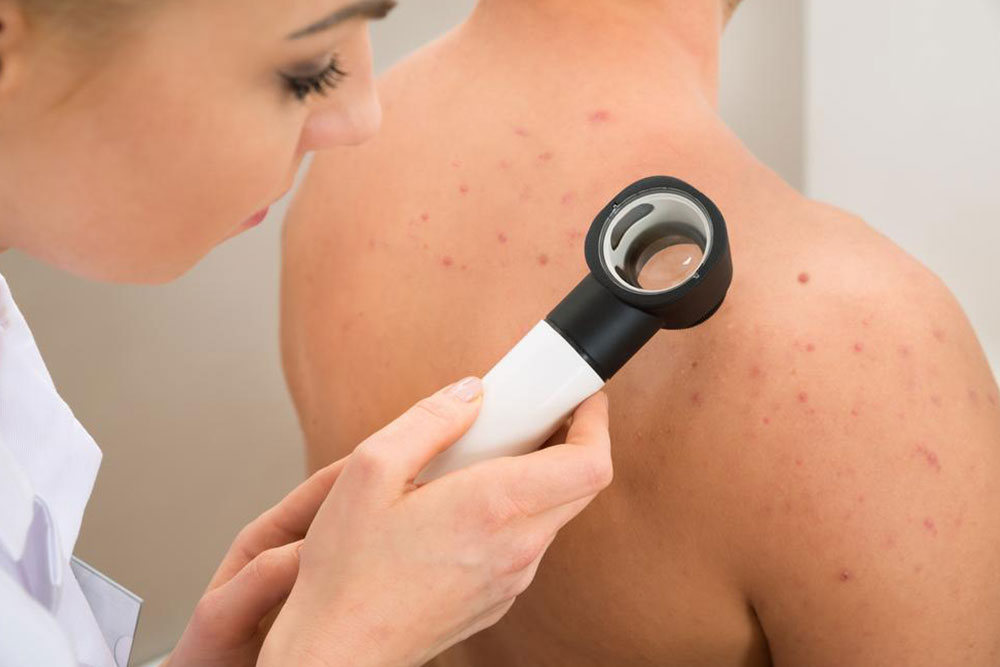
Fungal infections often affect the skin, particularly in warm, humid environments. These fungi thrive on keratin in skin, hair, and nails. Factors such as excessive sweating, public showers, swimming pools, and not changing socks or airing out shoes can increase infection risk. Use of antibiotics may also weaken skin's natural defenses. Practicing good hygiene, keeping skin dry, and avoiding prolonged moisture contact are key to preventing these infections. Awareness of common fungal conditions helps in early detection and management.
Good hygiene and avoiding excessive moisture are crucial in preventing fungal skin infections. Antibiotics can disrupt protective bacteria, making infections more likely. The main types include:
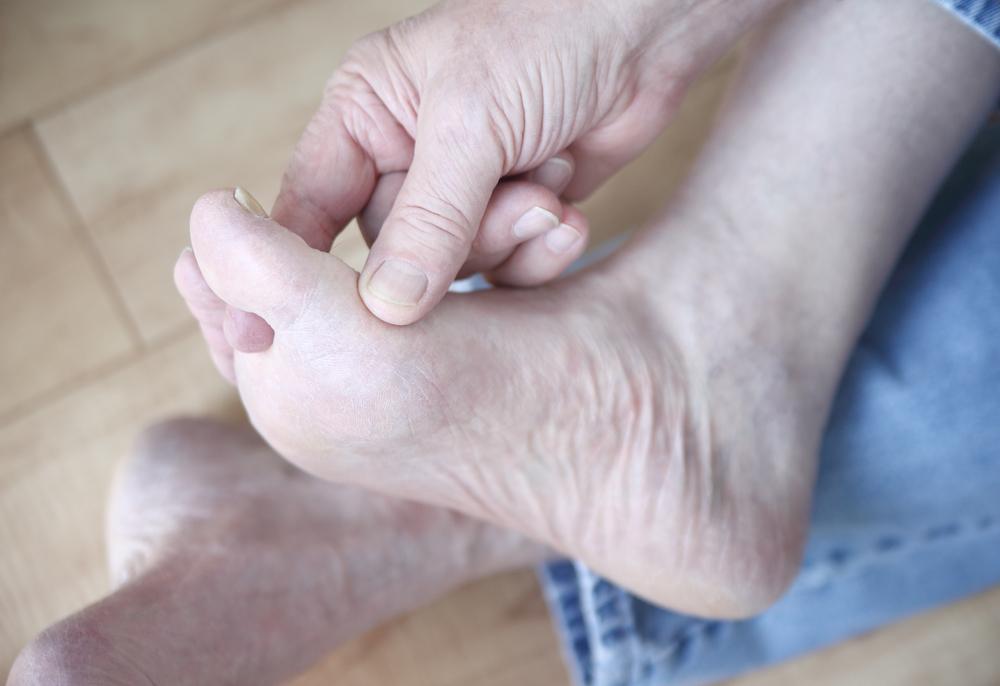
Athlete’s Foot: Tinea pedis affects feet and nails, causing peeling, cracking, blisters, redness, and itching. Skin may become soft or cracked.
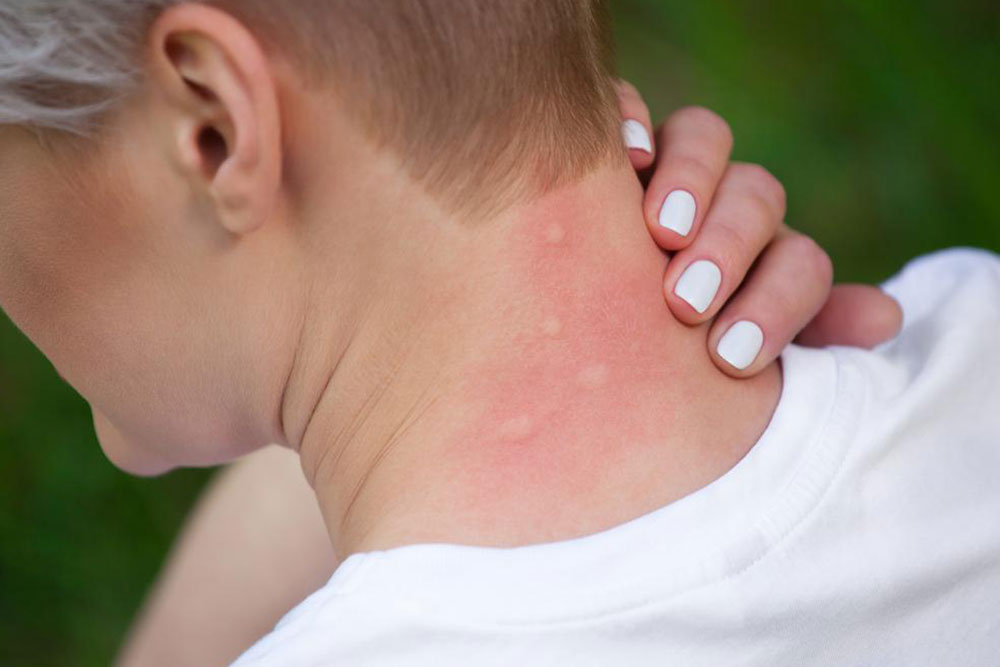
Jock Itch: Tinea cruris presents in the groin and inner thighs, with redness, chafing, circular rashes with raised edges, and itching.
Candidiasis: A yeast infection leading to rashes, pimples, pus-filled spots, and itching in affected areas, thriving in moist environments.
Pityriasis Versicolor: Also called tinea versicolor, causes painless, reddish-brown patches that alter skin color, common in teens and adults.
Ringworm: Tinea corporis appears as circular red lesions across the body, especially in hot, humid conditions. It is highly contagious.